(Leptocardii)
Lancelets
Ланцетникоподібні
The lancelets consist of 32 described species of “fish-like” benthic filter feeding chordates in the subphylum Cephalochordata, class Leptocardii, and family Branchiostomatidae.
Adult amphioxus typically inhabit the seafloor, burrowing into well-ventilated substrates characterized by a soft texture and minimal organic content. While various species have been observed in different types of substrate, such as fine sand, coarse sand, and shell deposits, most exhibit a distinct preference for coarse sand with low levels of fine particles.
(Appendicularia)
Larvaceans
Апендикулярії
Larvaceans, copelates or appendicularians, class Appendicularia, are solitary, free-swimming tunicates found throughout the world’s oceans. While larvaceans are filter feeders like most other tunicates, they keep their tadpole-like shape as adults, with the notochord running through the tail. They can be found in the pelagic zone, specifically in the photic zone, or sometimes deeper. They are transparent planktonic animals, usually ranging from 2 mm to 8 mm in body length including the tail, although giant larvaceans can reach up to 10 cm in length.
(Thaliacea)
Thaliaceans
Сальпи
Thaliacea is a class of marine chordates within the subphylum Tunicata, comprising the salps, pyrosomes and doliolids. Unlike their benthic relatives the ascidians, from which they are believed to have emerged, thaliaceans are free-floating (pelagic) for their entire lifespan. The group includes species with complex life cycles, with both solitary and colonial forms.
(Ascidiacea)
Sea Squirts
Асцидії
Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians or sea squirts, is a paraphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer test or “tunic” made of the polysaccharide cellulose.
Ascidians are found all over the world, usually in shallow water with salinities over 2.5%. While members of the Thaliacea (salps, doliolids and pyrosomes) and Appendicularia (larvaceans) swim freely like plankton, sea squirts are sessile animals after their larval phase: they then remain firmly attached to their substratum, such as rocks and shells.
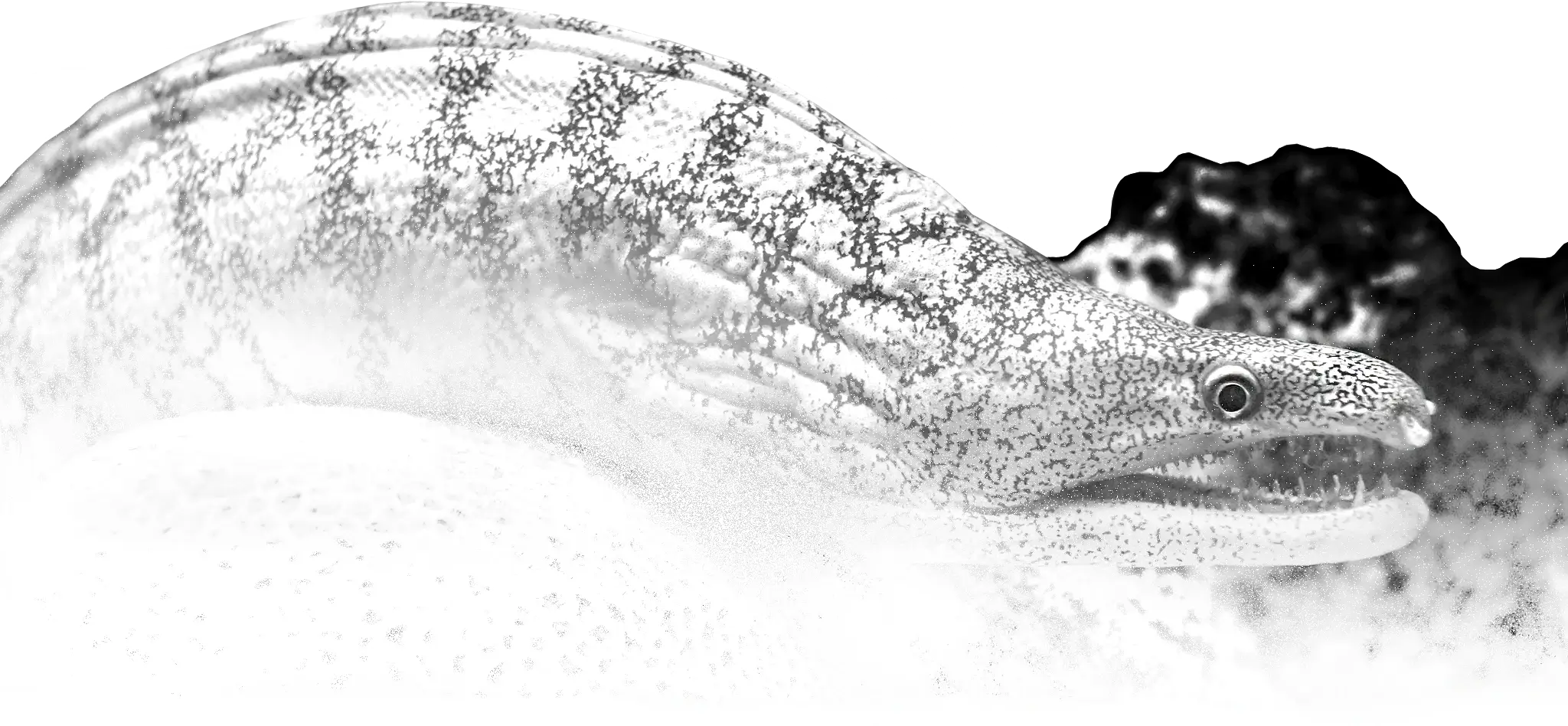
(Myxini)
Hagfish
Міксини
Hagfish, of the class Myxini, are eel-shaped jawless fish (occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, although they do have rudimentary vertebrae. Hagfish are marine predators and scavengers that can defend themselves against other larger predators by releasing copious amounts of slime from mucous glands in their skin.
(Petromyzontida)
Lampreys
Міногові
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of jawless fish comprising the order Petromyzontiformes, sole order in the class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterized by a toothed, funnel-like sucking mouth. About 38 extant species of lampreys are known, with around seven known extinct species. They are classified in three families – two small families in the Southern Hemisphere (Geotriidae, Mordaciidae) and one large family in the Northern Hemisphere (Petromyzontidae).
(Actinopterygii)
Ray-finned Fishes
Променепері
Actinopterygii, members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spines called lepidotrichia, as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles).
(Sarcopterygii)
Lobe-finned Fishes
Лопатепері
Sarcopterygii—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii —is a clade (traditionally a class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. These vertebrates are characterised by prominent muscular limb buds (lobes) within their fins, which are supported by articulated appendicular skeletons. This is in contrast to the other clade of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have only skin-covered bony spines supporting the fins.
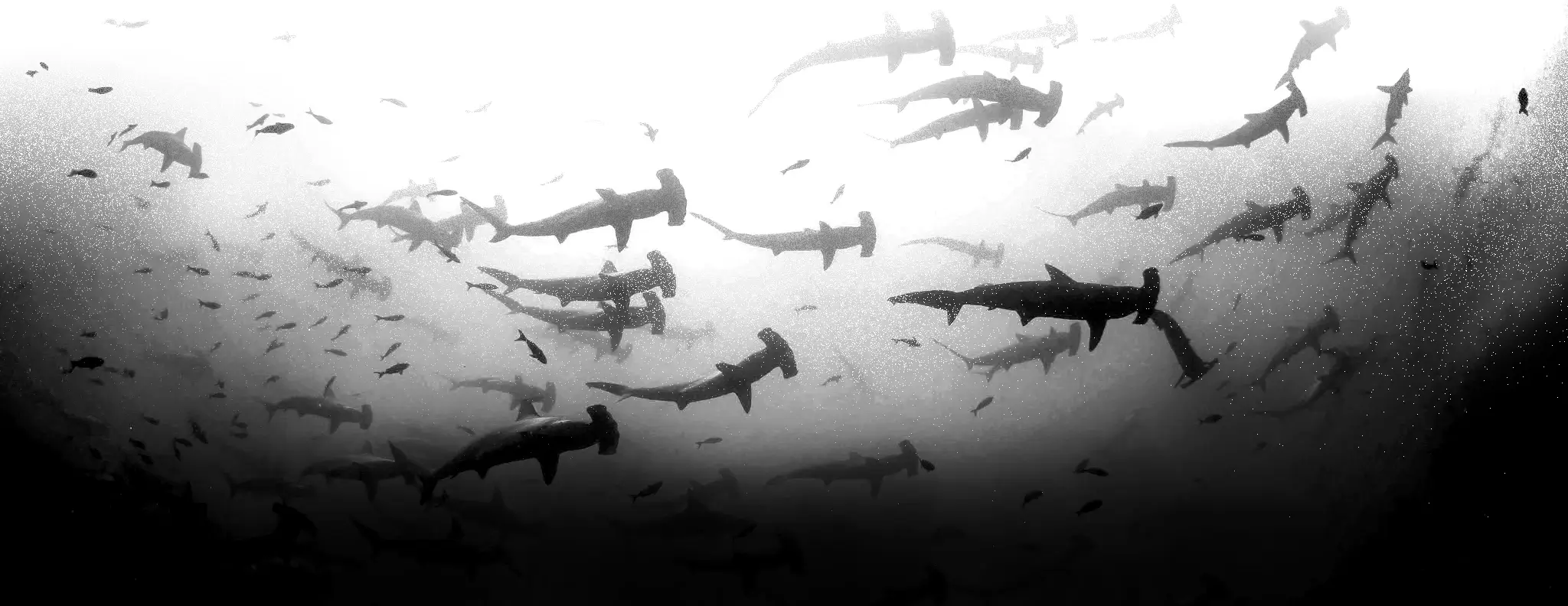
(Chondrichthyes)
Cartilaginous Fish
Хрящові риби
Chondrichthyes is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or bony fish, which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are aquatic vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, placoid scales, conus arteriosus in the heart, and a lack of opercula and swim bladders. Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates.

