(Porifera)
Sponges
Губки
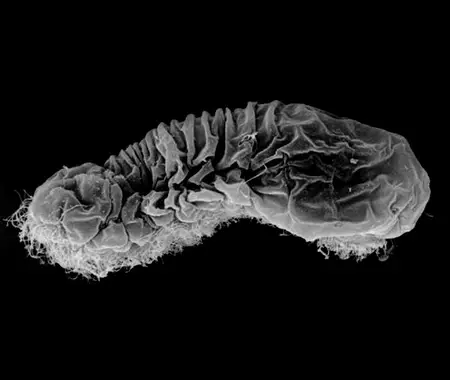
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the metazoan phylum Porifera, a basal animal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms.
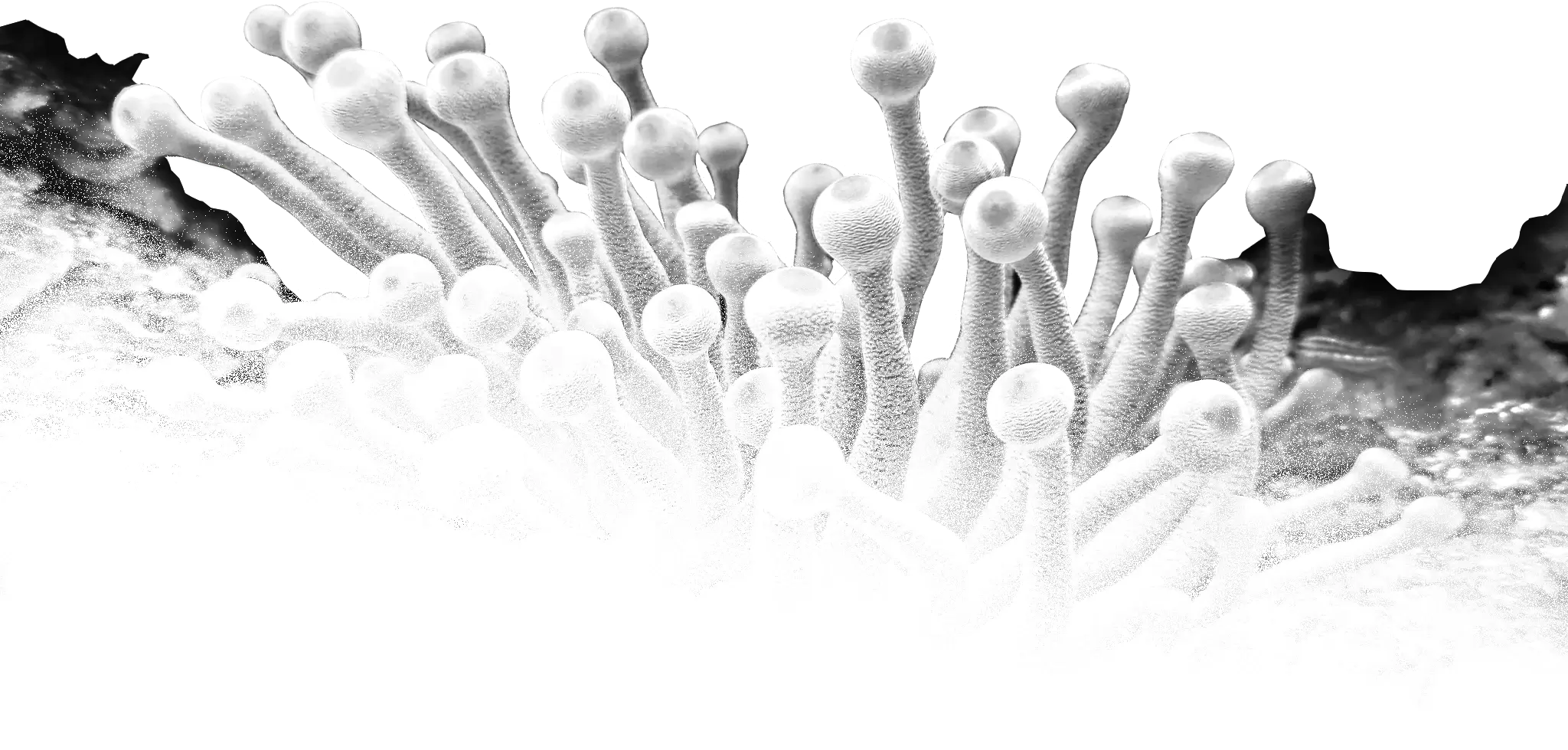
Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, heterotrophic, lack cell walls and produce sperm cells. Unlike other animals, they lack true tissues and organs. Some of them are radially symmetrical, but most are asymmetrical. The shapes of their bodies are adapted for maximal efficiency of water flow through the central cavity, where the water deposits nutrients and then leaves through a hole called the osculum. The single-celled choanoflagellates resemble the choanocyte cells of sponges which are used to drive their water flow systems and capture most of their food. This along with phylogenetic studies of ribosomal molecules have been used as morphological evidence to suggest sponges are the sister group to the rest of animals. A great majority are marine (salt-water) species, ranging in habitat from tidal zones to depths exceeding 8,800 m, though there are freshwater species. All adult sponges are sessile, meaning that they attach to an underwater surface and remain fixed in place (i.e., do not travel). While in their larval stage of life, they are motile.
Many sponges have internal skeletons of spicules (skeletal-like fragments of calcium carbonate or silicon dioxide), and/or spongin (a modified type of collagen protein). An internal gelatinous matrix called mesohyl functions as an endoskeleton, and it is the only skeleton in soft sponges that encrust such hard surfaces as rocks. More commonly, the mesohyl is stiffened by mineral spicules, by spongin fibers, or both. 90% of all known sponge species that have the widest range of habitats including all freshwater ones are demosponges that use spongin; many species have silica spicules, whereas some species have calcium carbonate exoskeletons. Calcareous sponges have calcium carbonate spicules and, in some species, calcium carbonate exoskeletons, are restricted to relatively shallow marine waters where production of calcium carbonate is easiest. The fragile glass sponges, with “scaffolding” of silica spicules, are restricted to polar regions and the ocean depths where predators are rare. Fossils of all of these types have been found in rocks dated from 580 million years ago. In addition Archaeocyathids, whose fossils are common in rocks from 530 to 490 million years ago, are now regarded as a type of sponge.
Although most of the approximately 5,000–10,000 known species of sponges feed on bacteria and other microscopic food in the water, some host photosynthesizing microorganisms as endosymbionts, and these alliances often produce more food and oxygen than they consume. A few species of sponges that live in food-poor environments have evolved as carnivores that prey mainly on small crustaceans.
Most sponges reproduce sexually, but they can also reproduce asexually. Sexually reproducing species release sperm cells into the water to fertilize ova released or retained by its mate or “mother”; the fertilized eggs develop into larvae which swim off in search of places to settle. Sponges are known for regenerating from fragments that are broken off, although this only works if the fragments include the right types of cells. Some species reproduce by budding. When environmental conditions become less hospitable to the sponges, for example as temperatures drop, many freshwater species and a few marine ones produce gemmules, “survival pods” of unspecialized cells that remain dormant until conditions improve; they then either form completely new sponges or recolonize the skeletons of their parents.
Habitats
Sponges are worldwide in their distribution, living in a wide range of ocean habitats, from the polar regions to the tropics. Most live in quiet, clear waters, because sediment stirred up by waves or currents would block their pores, making it difficult for them to feed and breathe. The greatest numbers of sponges are usually found on firm surfaces such as rocks, but some sponges can attach themselves to soft sediment by means of a root-like base.
Sponges are more abundant but less diverse in temperate waters than in tropical waters, possibly because organisms that prey on sponges are more abundant in tropical waters. Glass sponges are the most common in polar waters and in the depths of temperate and tropical seas, as their very porous construction enables them to extract food from these resource-poor waters with the minimum of effort. Demosponges and calcareous sponges are abundant and diverse in shallower non-polar waters.
Life Cycle
Sponges in temperate regions live for at most a few years, but some tropical species and perhaps some deep-ocean ones may live for 200 years or more. Some calcified demosponges grow by only 0.2 mm per year and, if that rate is constant, specimens 1 m wide must be about 5,000 years old. Some sponges start sexual reproduction when only a few weeks old, while others wait until they are several years old.
Source: Wikipedia